Causes
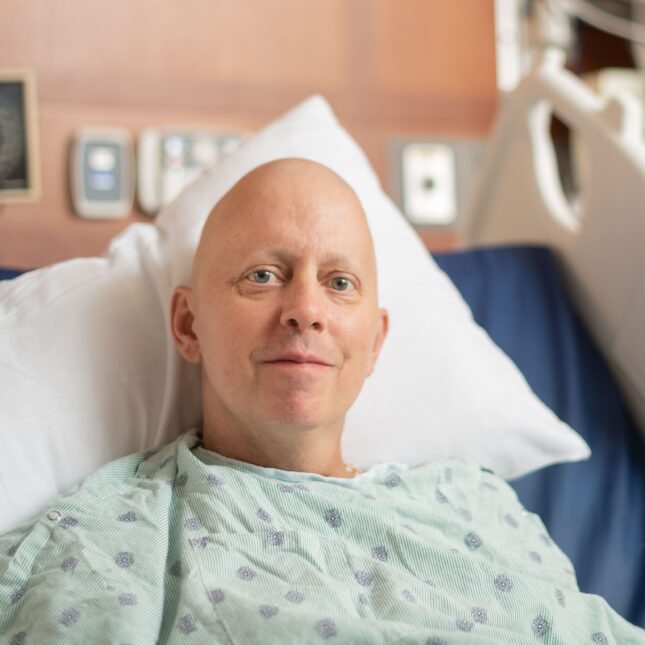
Cancer is a complex group of diseases that arise when abnormal cells in the body grow uncontrollably, potentially invading nearby tissues or spreading to other parts of the body. It can develop in almost any organ, with symptoms and outcomes varying widely depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
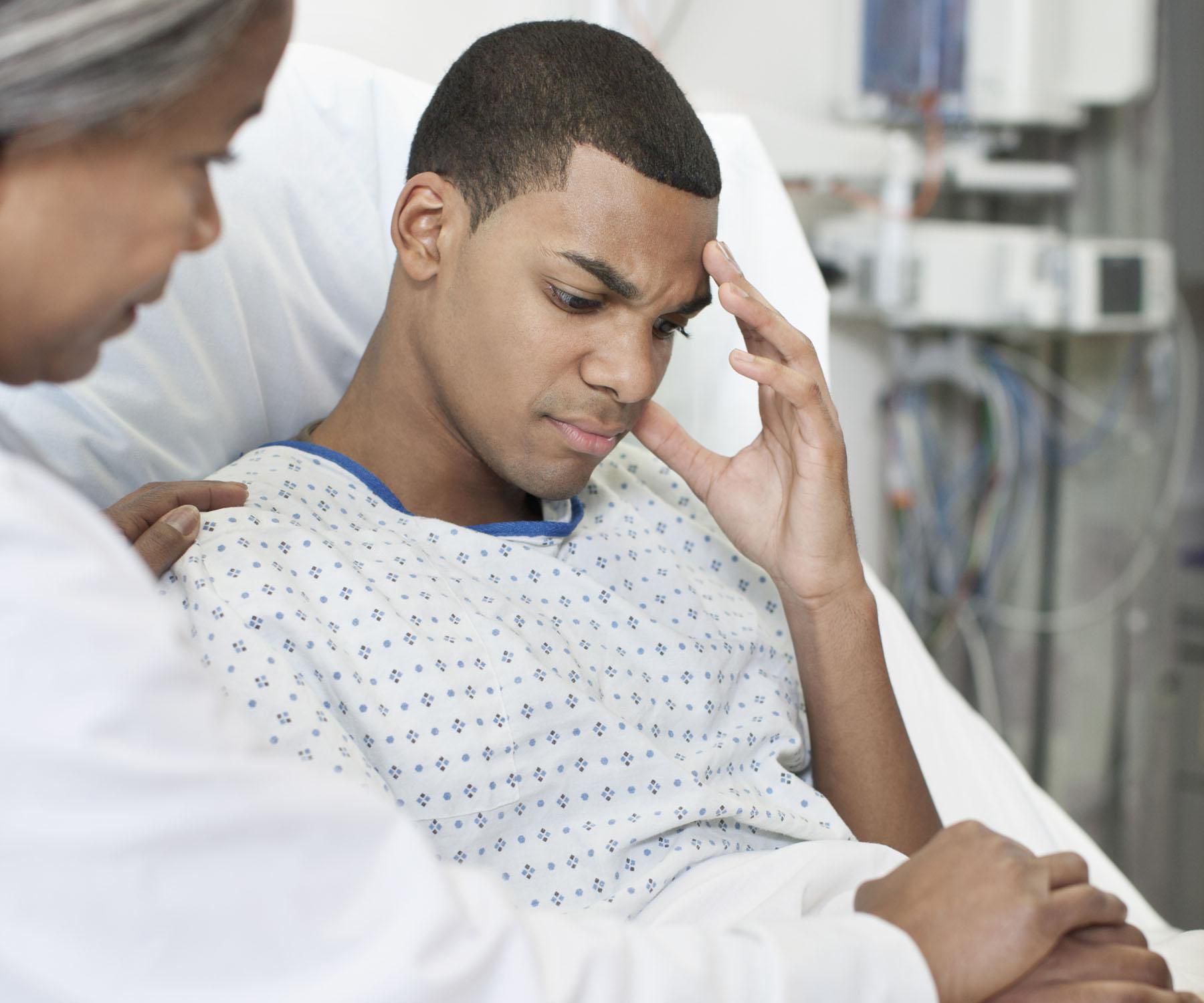

Neuro disorders affect the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. These disorders can result in many symptoms, including muscle weakness, paralysis, seizures, and headaches. While there are many different types of neuro disorders, they all share one commonality: they disrupt the normal function of the nervous system.
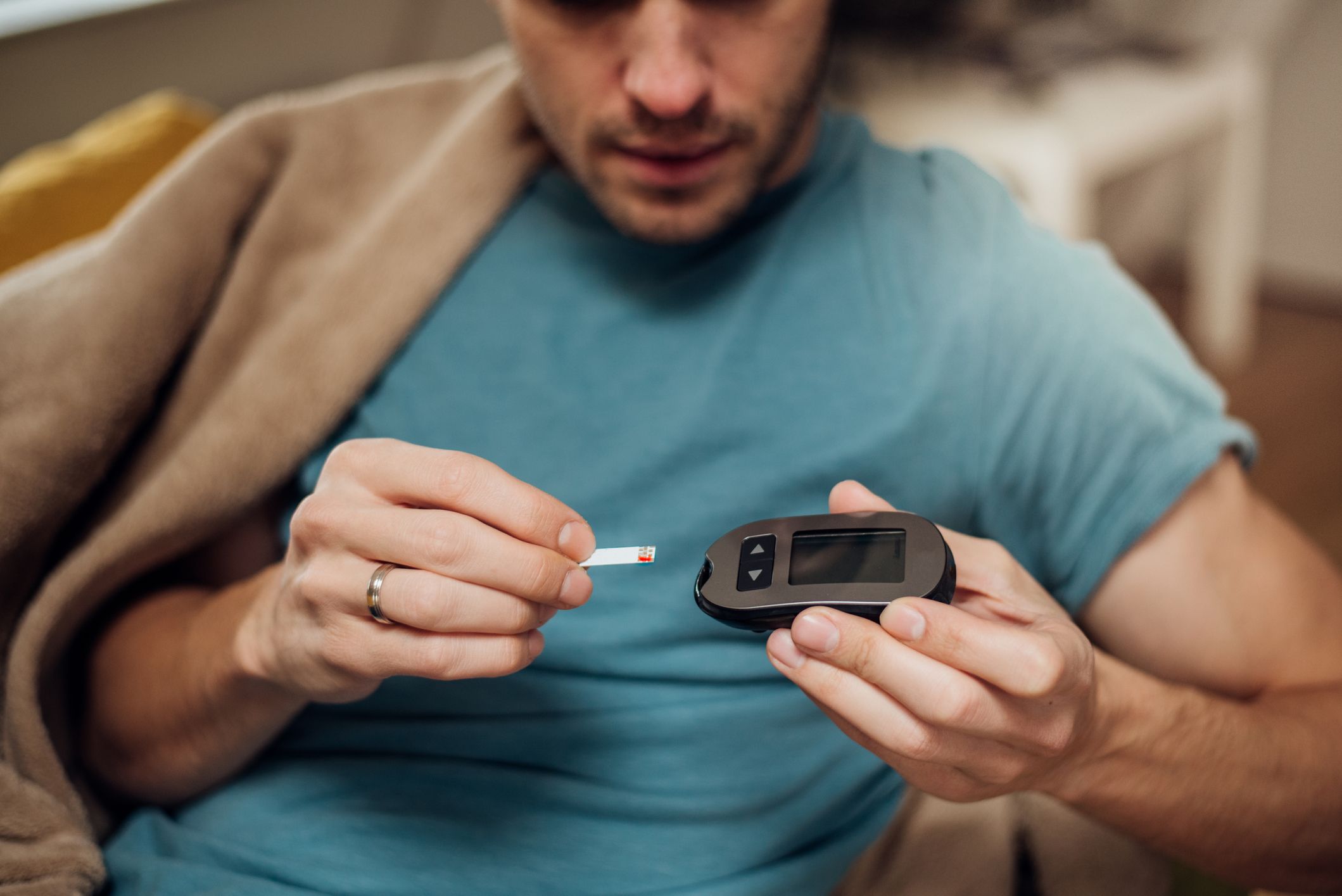

Genetic diabetes disorder (GDD) is a rare inherited condition affecting how the body metabolizes glucose. People with GDD have abnormally high levels of glucose in their blood, which can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, kidney failure, and blindness.
Medlineplus.gov – Phone – (1) 888-346-3656
- A health resource with a vast amount of health information and have been around for more than 25 years. They have lots of informative topics on several disease, also how genetics may affect your health.
Mayo Clinic.com – Phone – 507-266-7890/general number/24 hours
https://mayoclinic.org
UPMC Hillman Cancer Center (Pancreatic Cancer) – Phone – 412-530-5259
https://hillman.upmc.com
- One of the largest treatment centers in the U.S. based in Pittsburgh, PA..
American Diabetes Association – Phone – 1-800-342-2583
- The organization will help you find ways to pay for your healthcare, medication and treatment. Excellent Resource for Diabetes!
https://medschool.cuanschutz.edu
- Provides specialty care for military veterans, First Responders struggling with mild to moderate traumatic brain injuries.
- A great resources site, but they cannot provide medical or legal advice.
Envita Medical Centers – Phone – 602-569-4144
- A Holistic Cancer Treatment Center located in Scottsdale, AZ.

Let’s Help Children Build a Happy Future
Raised $08,500

Little Help Can Make a Big Difference
Raised $10,250
